Building Design
Primary tabs
These free videos, tutorials and case studies will help you apply concepts like daylighting, passive heating and cooling, and energy analysis to your projects in tools like Autodesk® Insight 360TM within Autodesk Revit®, and FormIt 360.
To design high performance buildings, you need to set concrete goals and follow a sound design process. Along the way you’ll need to optimize for both resource use and human comfort. Usually energy use is the largest environmental impact, and Net Zero Energy is an increasingly popular design goal.
Energy use is often the largest source of a building’s environmental impact. To improve your building’s energy efficiency, you need to understand its site, program, and energy loads.
Understanding heat transfer fundamentals and how they translate into energy flows in a building is critical when designing high performance buildings. Learn about the different forms of heat transfer, material properties like U-factor and R-value, heating and cooling loads, energy use intensity, and the difference between site and source energy.
The building envelope is the physical separator between the interior and exterior of a building. Components of the envelope are typically: walls, floors, roofs, windows, and doors. The design choices that you make and materials that you use for the envelope have a big impact on the building’s performance.
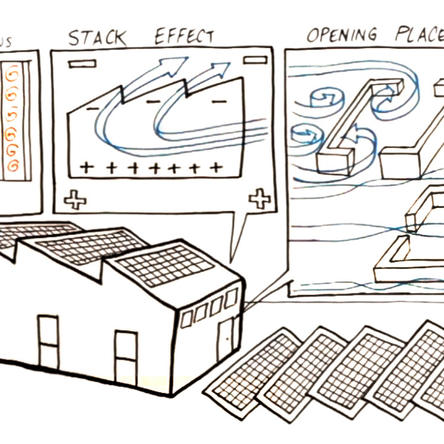
Passive design strategies can help reduce your building’s energy demands by using energy available from natural sources such as geothermal heat, sunlight, wind and cool air. Learn how to use convection, conduction, and radiation to design passive systems.
Getting smart about lighting is an important step to designing energy efficient buildings. Learn how to use daylighting, achieve proper light quality, and provide good controls to reduce energy demands and make people happier. The sun is predictable and daylight can be a very reliable source of light. Sunlight, views, and daylight are different though, and need to be carefully managed.
Mechanical Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems help keep building occupants comfortable when passive design strategies aren’t enough. To design efficiently, don’t oversize the system, choose efficient components, and optimize the whole system.
Water is used inside a building for drinking, cleaning, and sanitation, and outside of a building for landscaping. In addition, wastewater and runoff must also be managed for a sustainable building site.