energy
Software
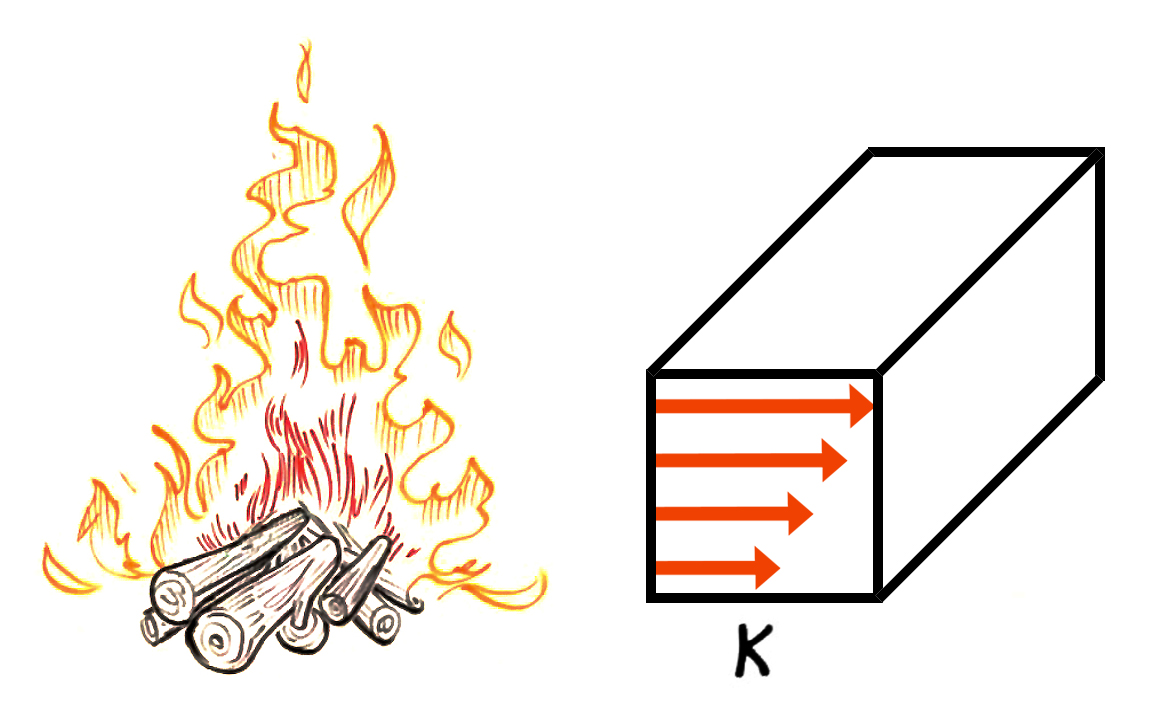
Every material has fundamental material properties that determine their energy performance like conductivity, resistance, and thermal mass. Knowing these terms will help you chose the right materials to improve heat flows.
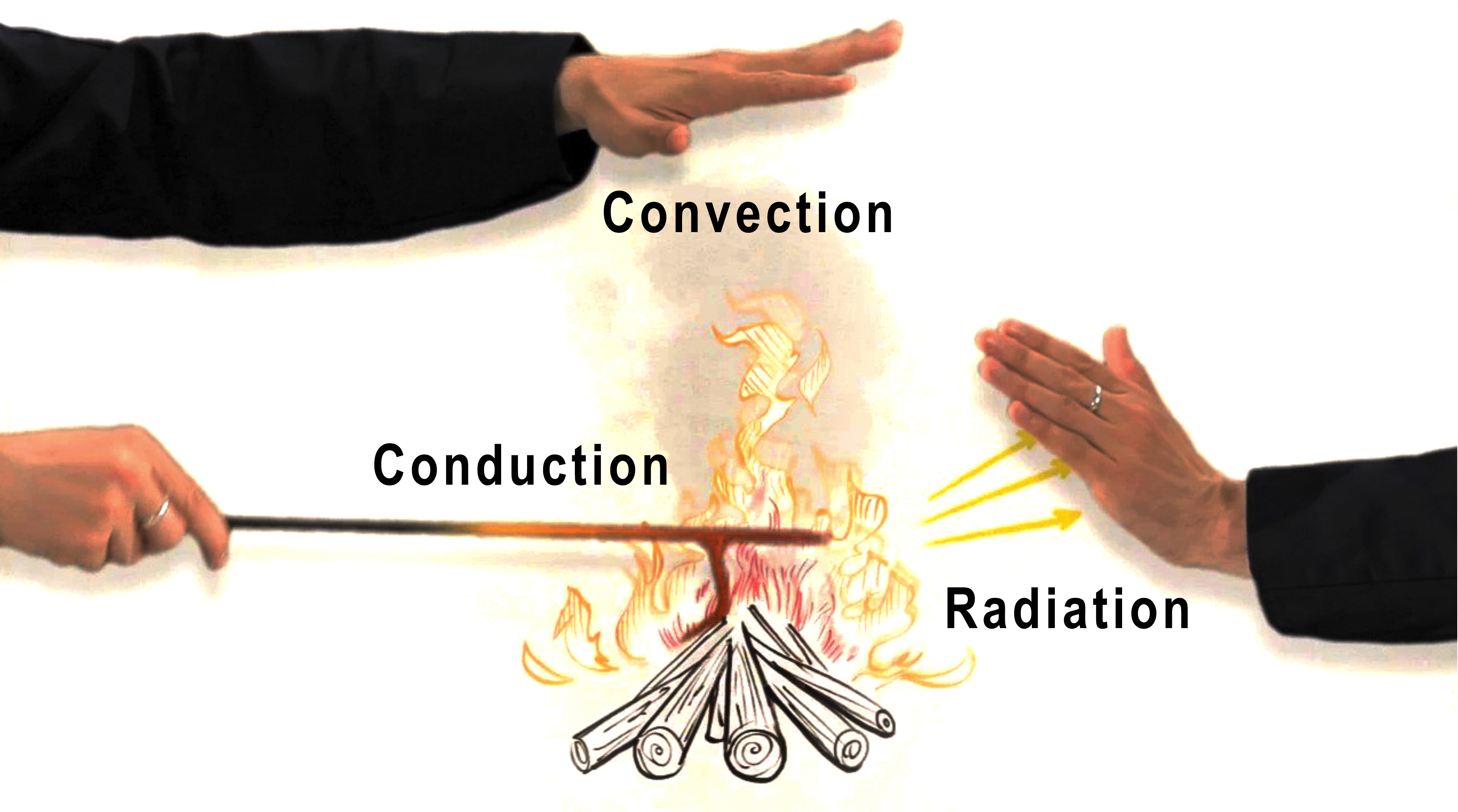
Understanding heat flows is key to creating energy efficient buildings. Understand latent heat vs. sensible heat and how heat is transferred via conduction, convection, and radiation.
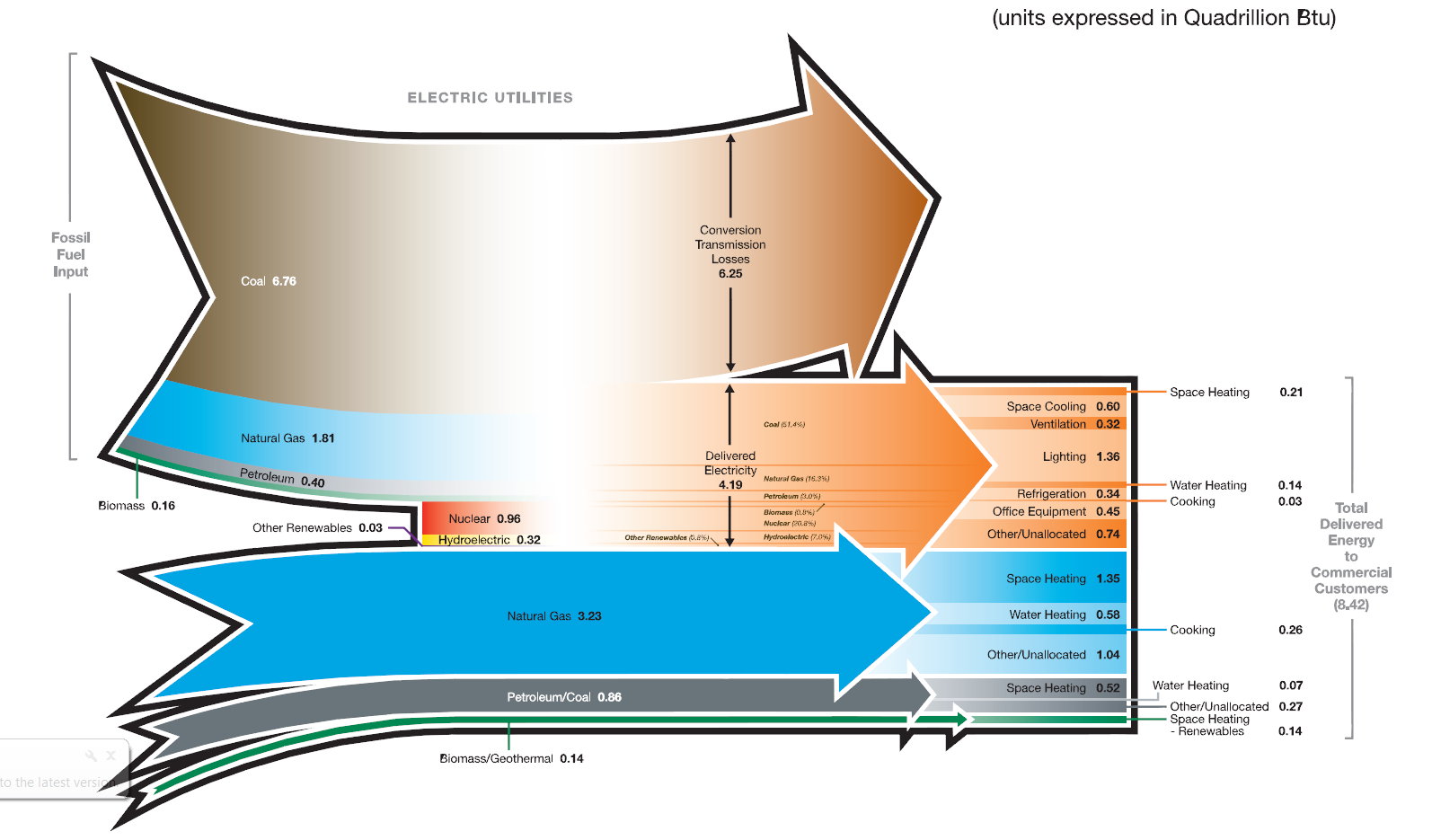
Knowing how to measure energy use in buildings will help you set better energy efficiency goals. Energy Use Intensity (EUI) normalizes energy use by floor area and is useful for targets and benchmarks. But, when it comes to environmental impacts, you need to look upstream at “source energy.” Also, when it comes to energy efficiency measures, you need to know what end-uses take the most energy.
Understanding heat transfer fundamentals and how they translate into energy flows in a building is critical when designing high performance buildings. Learn about the different forms of heat transfer, material properties like U-factor and R-value, heating and cooling loads, energy use intensity, and the difference between site and source energy.
Buildings use energy, materials, water, and land to create the right environment for their occupants. All of these things cost money – and all of them have an environmental impact.
Pages
Project Gallery Examples
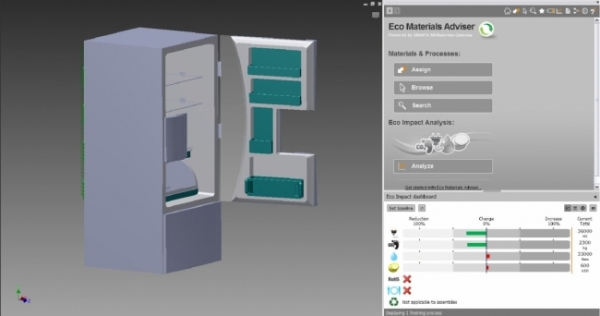
A team of engineering students developed a cost-competitive, environmentally friendly refrigerator. Learn about their results.
Autodesk used a new approach to building design called Integrated Project Delivery (IPD) for its AEC headquarters in Waltham, Massachusetts.
RMI’s headquarters uses a variety of methods to cut space heating by 99%, cut electricity use by 90%, and consume half as much water as a similar building.