Revit

Revit is Autodesk’s flagship BIM product. It is a full-featured parametric building information modeling platform for use throughout the design process. It has tools for architectural design, MEP design, and structural design.

When to use Revit
- Model conceptual designs, and do early energy analysis
- Model detailed design, including specification of building elements (walls, doors, windows, curtain walls).
- MEP design (pipe & duct layout)
- Lighting layout
- Documentation & detailing using typical views - plans, elevations, and sections.
Sustainable Design Functionality
- Export geometry into analysis packages like Ecotect or Green Building Studio using the gbXML file format.
- Conceptual energy analysis (within Conceptual Design Environment)
- Simulate and visualize lighting (qualitatively)
- HVAC load calculations
- Thermal properties of constructions. (But not specific thermal analysis within the tool).
- Track key quantities and eco-metrics in schedules (for example, the percentage of recycled materials in the project).
Software
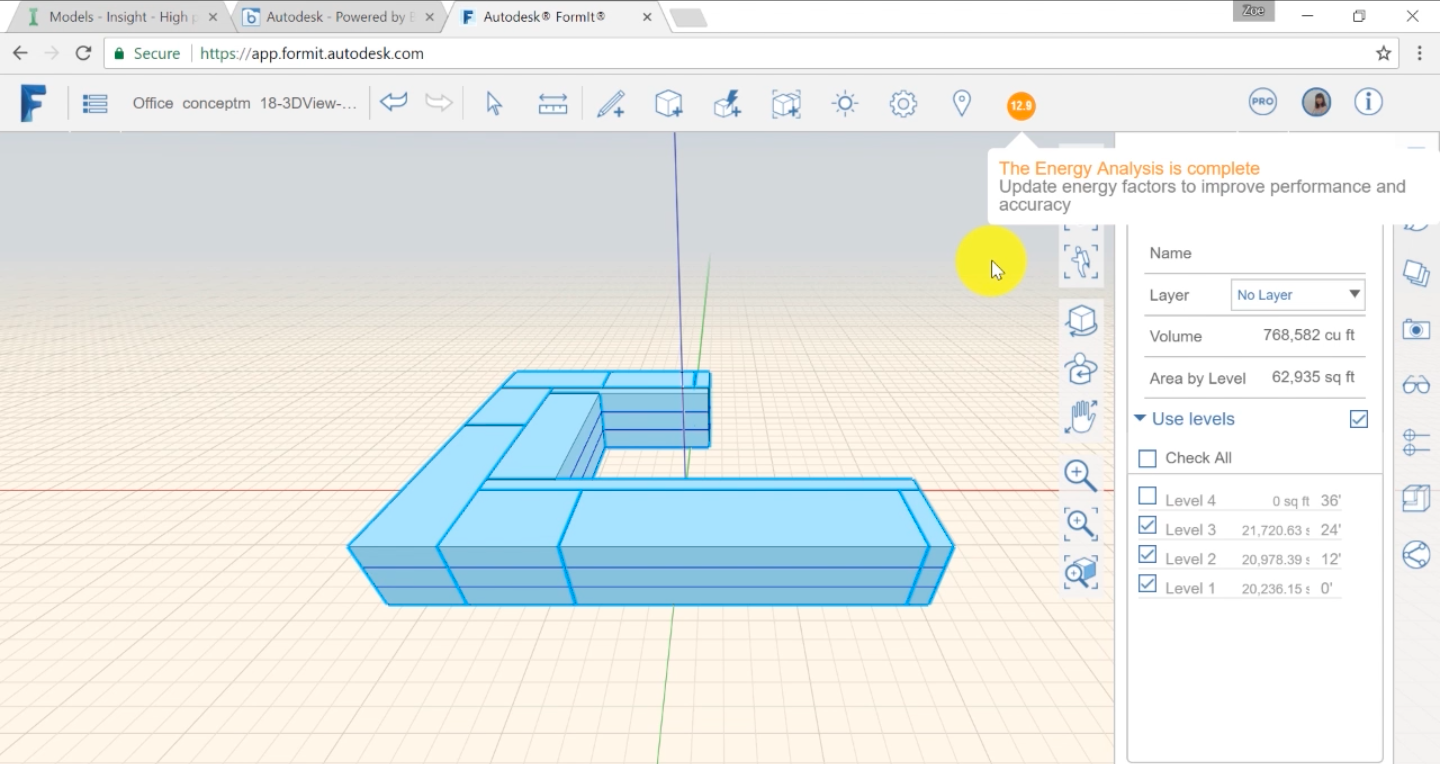
Generate an insight means performing an energy analysis on your model. The basic workflow presented in this video can be applied to all models but you’ll need to adapt and add to it to fit your model complexity and needs.
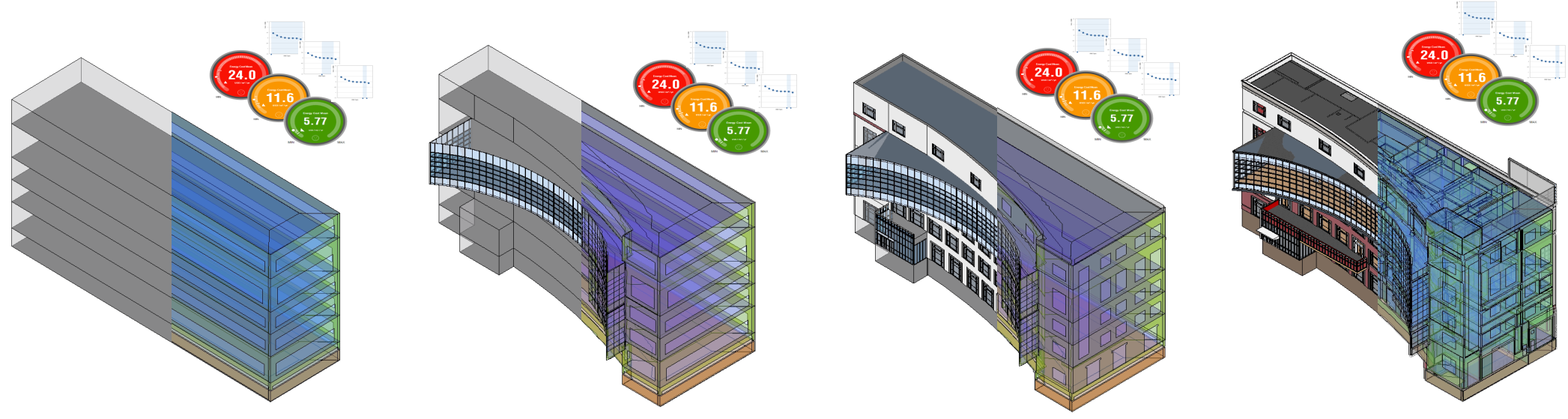
Autodesk provides tools that can help you analyze your building’s performance at all stages of the design process. These tools can help you to understand the factors that impact the building’s performance in order to make informed decisions about your design.
Software simulations can help you understand how heating and cooling loads change throughout the year, and what elements of your building’s design contribute the most. Is it excessive solar heat gain in the summer that makes you have to cool the space? Is that same heat gain helpful in cold winter months? What are the tradeoffs?
Being deliberate about your analysis process using BIM can go a long way towards both saving you time and improving the usefulness and validity of your results.
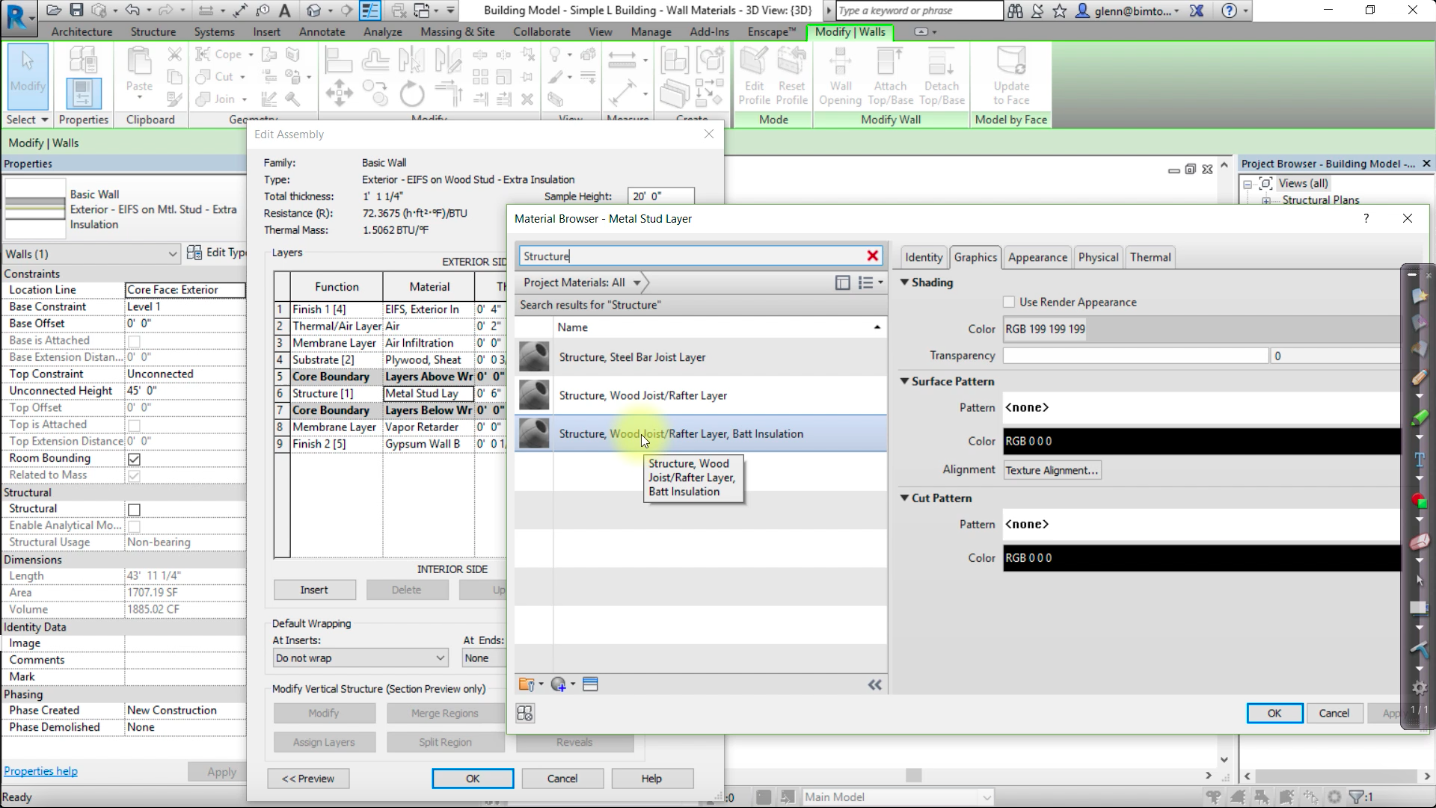
In Revit, you can customize the thermal properties of the wall, window, floor, and roof constructions to accurately reflect the materials that you would like to use in your design. These detailed properties can be exported in your energy model to be used as the As-Modeled Values in Insight by enabling the Detailed Element checkbox in the Advanced Energy Settings.
Pages
Project Gallery Examples
This winning high school team sought to design a net-zero school—one that produces as much energy as it consumes. Key to their approach was the selection of a site abundant in natural resources that could be harnessed for renewable energy, as well as the use of a variety of lesser-known energy-saving practices and techniques.
This project was an entrant in the June 2014 Excellence in Analysis Awards. The project used Revit to determine the amount of materials used in order to improve the building performance and calculate the embodied emission. The project’s presentation and concise documentation deserves an honorable mention.
A Russian student followed a rigorous and iterative process to design and analyze a mixed use conceptual building in Kazakhstan, winning the sustainable design prize in Autodesk’s 2013 global BIM competition.
This project used analysis throughout the design process to inform design decisions to improve energy use and return a school to the community as a symbol of the Italian village’s identity.
The visuals from this design project for a visitor center in Antelope Valley, California are a good example of using imagery to tell the story of design and performance analysis.